
News Center
New developments in newsWorld Tuberculosis Day | RAA Technology Enables Rapid Differentiation Between Tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium Complex Infections
 2025-03-31 08:40:56
2025-03-31 08:40:56
 56
56

Background and Significance
March 24, 2025, marks the 30th World Tuberculosis Day, with this year's theme being "Yes! We Can End TB: Commit, Invest, Deliver," emphasizing the commitment to ending tuberculosis (TB) through technological innovation and global collaboration. Despite progress in global TB control, significant bottlenecks remain in diagnostics:
Limitations of Traditional Methods
Smear Microscopy: Sensitivity of only 30-60%, unable to distinguish between Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) and nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM).
Liquid Culture: Time-consuming (2-6 weeks) and requires high biosafety levels (BSL-3).
Molecular Testing: While Xpert MTB/RIF is fast (2 hours), the equipment is expensive.
Diagnostic Challenges of NTM Infections
Pulmonary infections caused by NTM, such as Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC), present clinical symptoms highly similar to TB but require entirely different treatment regimens. Current clinical reliance on 16S rRNA sequencing or mass spectrometry is time-consuming and demands specialized platforms.
A breakthrough study published in Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology (2024) by a team from Shandong Second Medical University developed a novel detection method based on recombinase-aided amplification–lateral flow dipstick (Duplex RAA-LFD). This method can differentiate MTB from MAC in just 20 minutes, providing an efficient tool for clinical diagnosis. Below are the key findings from the study.
Technical Highlights: Duplex RAA-LFD Assay
RAA Technology: Isothermal nucleic acid amplification at 37°C, requiring no complex instruments, with results in 20 minutes.
LFD Dipstick: Visualized results, suitable for primary healthcare settings.
Innovative Breakthroughs
Dual-Target Design
Specific primers and probes were designed for MTB's IS6110 gene and MAC's DT1 gene, enabling simultaneous detection and differentiation.
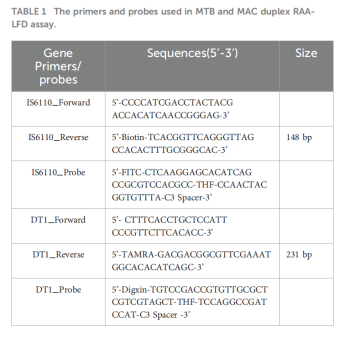
Labeling Strategy
MTB Test Line: Biotin-FITC labeling
MAC Test Line: TAMRA-Digoxin labeling
Result Interpretation: Presence of corresponding bands on the dipstick indicates a positive result.
Outstanding Performance
Sensitivity: Detection limit as low as 102 CFU/mL (superior to traditional culture).
Specificity: No cross-reactivity with 10 other mycobacterial species or common respiratory pathogens.
Clinical Validation: Tested on 60 suspected patient samples, showing 92.86% sensitivity and 93.75% specificity (using Xpert as the gold standard).
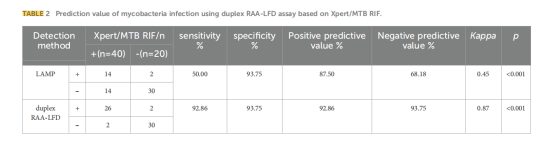
Advantages and Innovations
Speed: Entire process takes only 20 minutes, far faster than culture (2-6 weeks) or PCR (requiring thermal cycling).
Portability: No complex equipment needed, making it suitable for resource-limited areas.
Application Prospects
Primary Healthcare: Can be deployed in community clinics or remote areas without expensive equipment.
Infection Control: Rapid differentiation between MTB and MAC prevents mistreatment and drug resistance risks.
Expansion Potential: The framework can be adapted for detecting other pathogens, such as drug-resistant genes or co-infections.
Insights from World Tuberculosis Day
Innovations in diagnostic technology are key to ending TB. As demonstrated in this study, point-of-care testing (POCT) tools like RAA-LFD can address the shortcomings of traditional methods. Global collaboration must accelerate technology transfer to promote the adoption of low-cost solutions in high-burden countries.
Take Action:
Raise awareness about TB prevention and treatment to enhance public understanding!


WeChat Official Account


Service Hotline:
0510-85385531Telephone:
18921157475Address:
4-5F, Building B, Xingye Building, No. 97 Linghu Avenue, Xinwu District, Wuxi CityF
